The degree in Electronic Engineering comes around in the year 2000 due to the need in the productive sector to count on professionals capable of taking forward the control of industrial plants, the installation and maintenance of electrical equipment, the use and programming of applications in real time in the industry, as well as the installation and maintenance of telecommunication systems and networks.
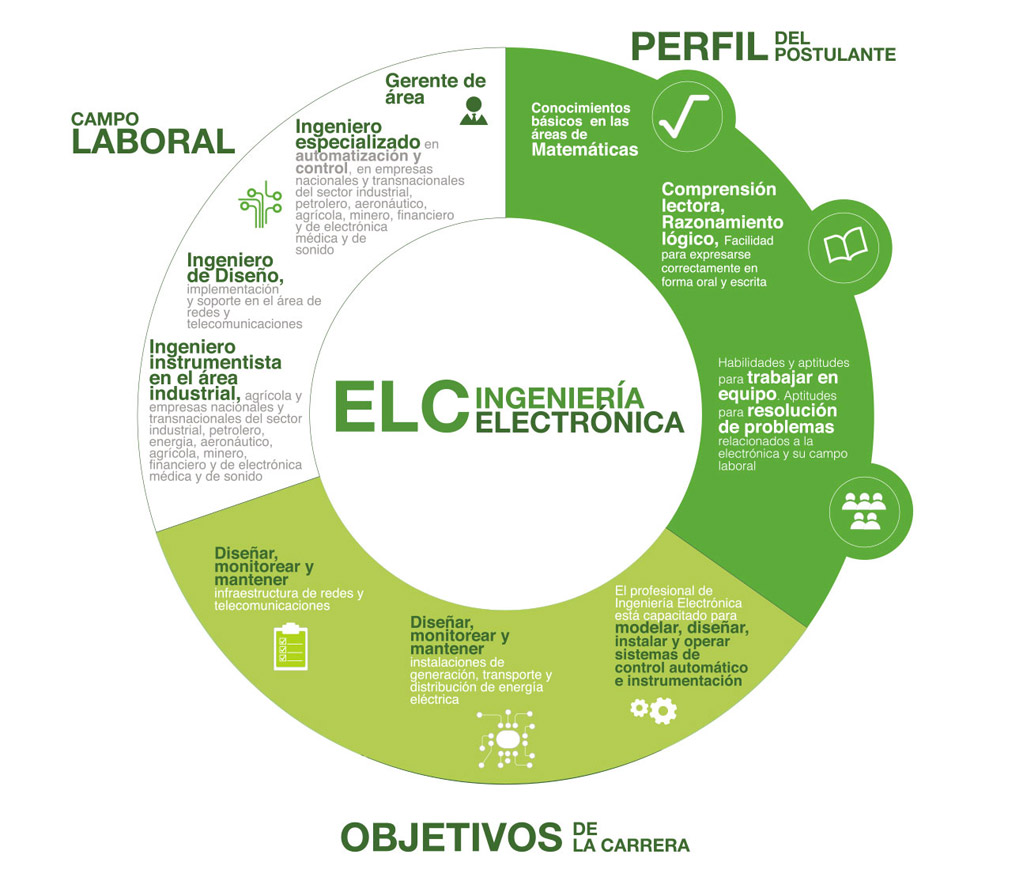
The UPSA Electronic Engineer is a capable professional, able to model systems of automatic control, design projects for industrial automation from the electrical-electronic point of view, resolve problems in the industry related to the automation related to automatic control, understand and apply the tools and/or devices for automation from an electronic, electrical and industrial point of view, programming control devices such as PLC through the use of programming languages that are appropriate to these devices, determine what software is adequate to control automation in an industry, apply the knowledge in Electrical Engineering to evaluate and /or carry out electrical industrial installations, manage and evaluate projects in Electronic Engineering and installing and maintaining telecommunications systems. To provide support in this technical training area, the University has several computer laboratories and specific electronics laboratory.
As an Electronic Engineer you will be able to become an area Manager, Project Director or specialized Engineer in automation and control, in national and international companies in the industrial, petroleum, aeronautic, agricultural, mining, financial and medical electronic and sound sectors; design systems for automatic control, applying industrial high quality tools and carrying forth the installation of high quality installations and maintenance of electronic equipment.
You will also be able to create your own company and prepare projects in robotics and automation, model systems for automatic and instrumentation control, resolve problems in industrial processes, program PLC and implement SCADA systems using micro-controllers such as Arduino and PIC.
Plan
de
estudios
| PRIMER SEMESTRE | Fundamentos de Matemática | Fundamentos de la Administración de Empresas | Álgebra I | Fundamentos de TI | Pensamiento Crítico | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SEGUNDO SEMESTRE | Calculo I | Mecánica | Álgebra II | Redes I | Electrónica Digital | Fundamentos de Programación | |
| TERCER SEMESTRE | Calculo II | Fluidos, Calor y Sonidos | Química General | Redes II | Sistemas Digitales | Estructura de Datos | |
| CUARTO SEMESTRE | Calculo III | Electromagnetismo y Ondas | Cableado Estructurado | Electrónica I | Programación Aplicada | Interculturalidad, Ciudadanía y Género | |
| QUINTO SEMESTRE | Ingeniería de Control I | Circuito I | Telecomunicaciones I | Laboratorio de Redes I | Electrónica II | Certificación Idioma Inglés | |
| SEXTO SEMESTRE | Ingeniería de Control II | Circuito II | Telecomunicaciones II | Instrumentación I | Ética y Valores | ||
| SÉPTIMO SEMESTRE | Seguridad y Mantenimiento Industrial | Instalaciones de Baja y Media Tensión | Máquinas Eléctricas I | Laboratorio de Redes II | Instrumentación II | Electiva I | Pasantía Profesional (300 hrs) |
| OCTAVO SEMESTRE | Robótica Industrial | Centrales Eléctricas | Máquinas Eléctricas II | Laboratorio de Redes III | Sistemas en Tiempo Real | Electiva II | |
| NOVENO SEMESTRE | Control Digital | Subestaciones Eléctricas | Modalidad de Grado I | Electrónica Industrial | |||
| DÉCIMO SEMESTRE | Modalidad de Grado II |
Materias
Electivas
-
Sistemas Operativos
-
Estructura de Datos Avanzadas
-
Laboratorio de Sistemas Operativos I
-
Base de Datos
-
Resistencia de Materiales
-
Elementos Mecánicos
-
Estadística II
-
Investigación Operativa I
-
Investigación Operativa II
-
Contabilidad General I
-
Contabilidad General II
-
Teoría de la Organización
-
Psicología Social
-
Writing Lab
-
Life Plan To Excellence
-
TecnoUPSA Feria de Ciencias y Tecnología
-
Capítulo Estudiantil IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronis Engineers)
-
Feria de Emprendimiento